I. The USB-C Revolution: More Than Just a Pretty Port
The humble USB-C port. It's more than just a connector, isn't it? It's a gateway, a portal if you will, to a world of powerful charging capabilities and rapid data transfer speeds. This small, reversible marvel was designed with a vision of universality in mind. Yet, beneath its sleek, compact form lies a complexity that often leaves users scratching their heads.
The promise was simple: one cable to rule them all. One cable to charge your phone, your laptop, your headphones. But the reality, as is so often the case, is far more nuanced. The physical connector is indeed universal; that much is true. However, the standardsthat it supports, the protocols it speaks, are anything but. To truly appreciate the magnitude of this shift, cast your mind back to the era of bulky, proprietary chargers, each tailored to a specific device. Remember those days of rifling through drawers, searching for the one charger that fit? USB, in its initial iterations, offered a glimmer of hope, providing a basic charging solution. But it was slow, underpowered, and still a far cry from the truly universal solution we craved.
II. The Charging Titans: A Head-to-Head Battle
Within the USB-C ecosystem, several charging standards vie for dominance, each with its own history, strengths, and weaknesses. Let's examine some of the key players.
-
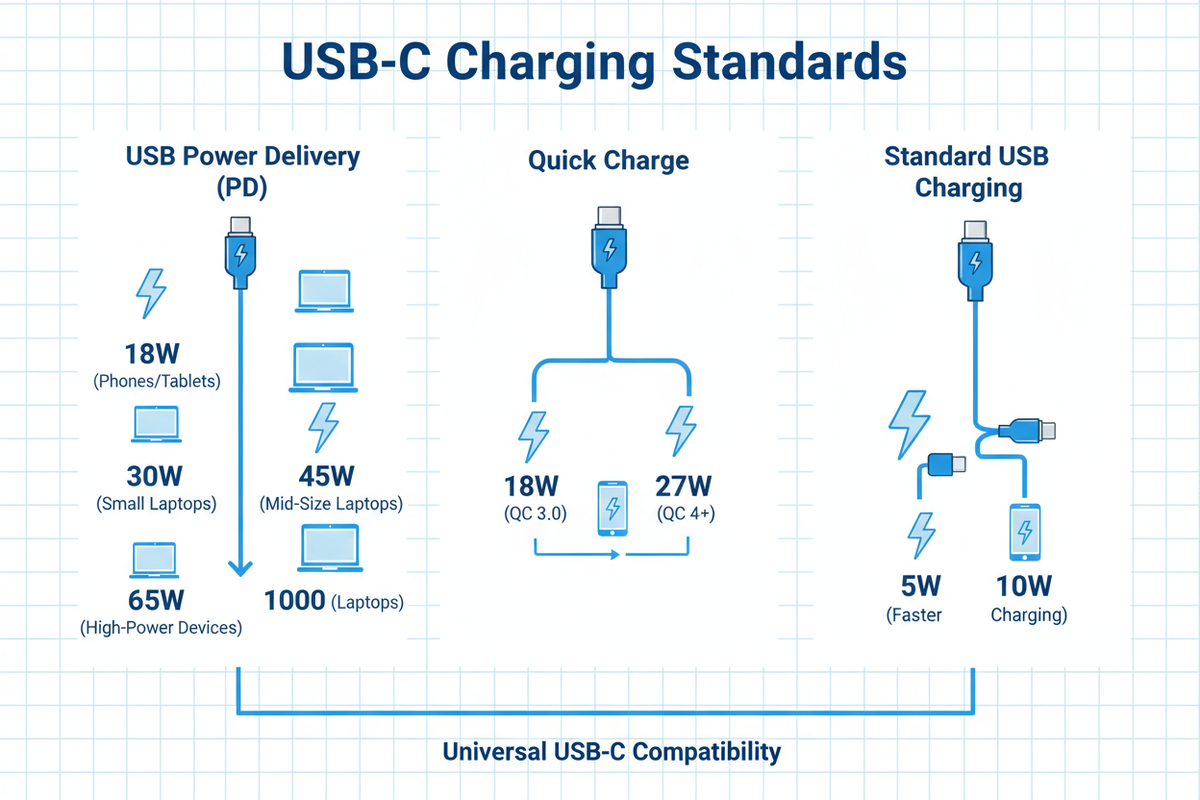
USB Power Delivery (USB PD): The Open Standard Champion
Born from the inherent limitations of earlier USB iterations, USB PD emerged as an open standard designed to deliver significantly more power. It is in constant evolution, with versions like PD 3.1 and the introduction of Extended Power Range (EPR) pushing the boundaries of what's possible. The beauty of USB PD lies in its intelligent negotiation. Devices and chargers engage in a subtle dance, "talking" to each other to determine the optimal voltage and current for efficient charging. One of its standout features is its incredible power capacity, reaching up to 240W. Beyond raw power, USB PD offers bidirectional power flow and the clever Programmable Power Supply (PPS) feature, which allows for fine-tuned, battery-friendly charging. This universal compatibility, championed by brands like Apple, Google, and Samsung, is a considerable advantage. The pursuit of standardization ultimately reduces e-waste and promotes intelligent power management. The Achilles' heel of USB PD lies in cable compatibility. Not all USB-C cables are created equal, and many lack the necessary certifications to support the full power capabilities of PD, leading to widespread user confusion.
-
Quick Charge (QC): Qualcomm's Android Powerhouse
Qualcomm's Quick Charge (QC) arose as a proprietary solution to meet the demands of faster charging, inextricably linked to the Snapdragon chipsets found in many Android devices. From the early days of QC 2.0, which delivered a respectable 18W, it has evolved into QC 5, boasting capabilities exceeding 100W with claims of charging speeds of up to 50% in 5 minutes. Interestingly, the most recent versions of QC have begun to embrace USB PD PPS, signaling a potential convergence of standards. The primary advantage of QC is its blazing-fast charging speeds for compatible Android devices, coupled with backward compatibility with older versions. On the downside, its historically proprietary nature resulted in limited compatibility across different brands and further contributed to user confusion, especially when paired with USB-C ports.
-
SuperVOOC (OPPO) & Warp Charge (OnePlus): The Amperage All-Stars
Sharing a common ancestry, OPPO's SuperVOOC and OnePlus's Warp Charge represent a different approach to fast charging. These technologies prioritize high amperage and lower voltage, effectively shifting the heat generation from the phone to the adapter. This often involves the use of split battery designs within the phone itself. The results are truly impressive, with charging speeds reaching up to 240W in demonstrations and more commonly delivering between 65W and 100W, allowing for a full charge in a matter of minutes. However, these technologies are highly proprietary and limited to specific brands, such as OPPO, OnePlus, Realme, and Vivo, requiring the use of specific cables and adapters to achieve their advertised charging speeds.
-
Samsung Adaptive Fast Charging (AFC): The Legacy Player
Samsung's Adaptive Fast Charging (AFC) has its roots in Quick Charge 2.0, delivering up to 15W of power. However, recognizing the need for more advanced charging capabilities, Samsung has embraced USB PD 3.0 with PPS in its newer "Super Fast Charging" implementations, demonstrating a commitment to open standards. While AFC remains a reliable option for older Samsung devices, its limited power output pales in comparison to newer charging standards, and it is increasingly being replaced by USB PD.
III. The Battlegrounds: Current Opinions and Lingering Controversies
Despite the progress made in USB-C charging, several controversies persist, fueling debate and frustrating consumers.
-
The "Cable Chaos" Conundrum
"Why doesn't this USB-C cable work with thatcharger?" This lament echoes across forums and comment sections, a testament to the pervasive confusion surrounding USB-C cables. The problem lies in the deceptively similar appearance of cables with vastly different capabilities. Some cables are designed solely for basic charging, while others support high-speed data transfer, video output, and high-wattage charging. The critical role of E-Marked cables, which contain an electronic chip that identifies their capabilities, is often overlooked, leading to mismatched expectations and suboptimal charging experiences.
-
Proprietary vs. Open: The Eternal Tug-of-War
The debate between proprietary and open standards lies at the heart of the USB-C charging landscape. The promise of USB PD, with its universal compatibility, reduced e-waste, and increased consumer choice, aligns with the EU's mandate for USB-C, representing a significant step towards a more standardized future. Proponents of proprietary standards argue that they enable faster innovation and allow companies to differentiate their products. However, this often comes at the cost of reduced compatibility and slower charging speeds when using generic chargers.
-
Safety First (Hopefully!): The Risks of Bad Cables & Chargers
The market is flooded with cheap, uncertified cables and chargers that pose significant safety risks. Voltage and current mismatches, overheating, damaged components, and even fire hazards are all potential consequences of using substandard products. Modern standards like PPS and the use of high-quality components can help mitigate these risks, but consumers must remain vigilant and exercise caution when purchasing charging accessories.
IV. The Road Ahead: What's Next for USB-C Charging?
The future of USB-C charging is bright, with several promising developments on the horizon.
-
The Reign of USB PD 3.1 & Extended Power Range (EPR)
The introduction of USB PD 3.1 and Extended Power Range (EPR) marks a significant step forward, enabling power delivery of up to 240W. This opens up new possibilities for powering laptops, monitors, and even power tools via USB-C, potentially eliminating the need for bulky proprietary barrel connectors. Adjustable Voltage Supply (AVS) promises even more intelligent power delivery, further optimizing charging efficiency and battery health. Enhanced safety protocols are also being implemented to ensure the safe delivery of higher power levels.
-
Beyond Phones: Industrial & Automotive Applications
USB-C PD is expanding its reach beyond consumer electronics, finding applications in industrial and automotive settings. From powering robots and industrial displays to serving as a key component in EV charging infrastructure, USB-C PD is poised to become a ubiquitous power delivery solution.
-
GaN Chargers: Smaller, Faster, Cooler
Gallium Nitride (GaN) technology is revolutionizing charger design, enabling the creation of smaller, more efficient chargers that support high power output without the bulk of traditional silicon-based chargers.
-
The EU's Influence: A Truly Universal Future?
The European Union's mandate for USB-C as the universal charging standard for electronic devices, including laptops by 2026, is a pivotal moment in the quest for standardization. This initiative is expected to drive further innovation and reduce e-waste by promoting the adoption of detachable cables on charging bricks.
-
Smarter, Safer, More Integrated
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into Battery Management Systems (BMS) promises optimized charging algorithms that can extend battery lifespan and enhance safety. Further integration with wireless charging technologies like Qi2.2 is also expected, blurring the lines between wired and wireless charging. The ultimate goal is a future where a single, high-quality, smart USB-C charger can efficiently and safely power every device you own.
V. Your Charging Survival Guide: Don't Get Zapped by Confusion!
Navigating the complexities of USB-C charging can be daunting, but by following these simple guidelines, you can ensure a safe and efficient charging experience:
- Read the Specs: Always verify the power delivery capabilities supported by your device, charger, and cable.
- Invest in Quality: Choose certified cables and adapters from reputable brands.
- Match Makers: For proprietary fast charging technologies, use the manufacturer's recommended charger and cable.
- Embrace USB PD/PPS: For maximum compatibility and efficiency, USB PD with PPS is the preferred option for most devices.
The journey towards universal charging is still underway. USB-C continues to evolve, promising a simpler, more powerful, and safer charging experience for all.